At Afri India Medil, our patients have expressed their appreciation for the skilled doctors who have helped them regain their lost confidence. They can now live life without worrying about their appearance, reflecting our mission to spread happiness!
Before embarking on a hair transplant treatment, plastic surgeons typically conduct routine blood tests for all patients. These tests include CBC, HCV, Random Blood Sugar, HBs, ECG, and HIV ELISA. They are essential for detecting and ruling out any underlying medical issues that could complicate the surgical outcome.
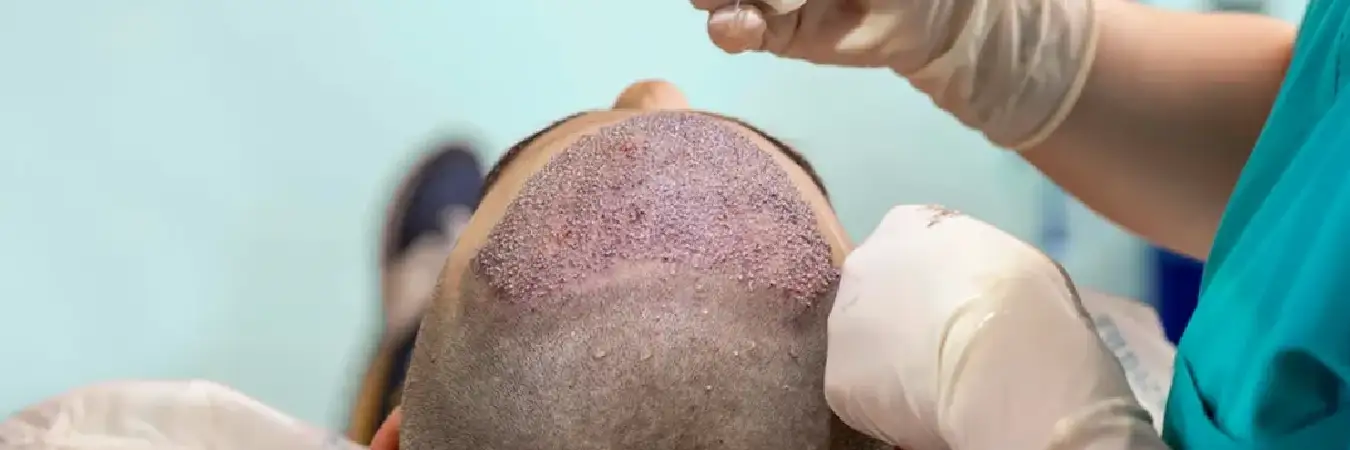
In hair transplantation, small grafts containing hair-bearing scalp or larger scalp sections from the donor site are excised and relocated to bald or thinning areas of the scalp. The grafts can vary in shape and size, and several techniques can be employed to perform hair transplant surgery.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
In FUT, the surgeon first administers local anesthesia to numb the back of the head for a painless experience. The surgeon then sterilizes the donor site from which the hair will be taken.
A scalpel, a medical instrument, is employed to remove a section of scalp from the back of the head, which is then closed using surgical sutures.
The excised scalp is divided into as many as 2,000 tiny grafts using a scalpel.
Small incisions are made in the recipient area of the scalp where the hair will be transplanted using needles.
The surgeon inserts the small grafts into these incisions through a process called grafting and closes the surgical sites with bandages.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
In Follicular Unit Extraction or FUE, the surgeon directly extracts hair follicles from the back of the head through tiny punch incisions.
Initially, the surgeon shaves the back of your head, and local anesthesia is applied to numb the area.
The extraction process involves removing individual hair follicles from the shaved portion of your scalp.
Subsequently, small incisions are made in the remaining scalp, and hair follicles are precisely grafted. The surgeon covers the surgical site with a bandage.
Direct Hair Implantation (DHI)
In DHI, the surgeon shaves the donor area and the back of the head.
Local anesthesia is administered to numb the scalp, ensuring a painless procedure.
A specialized medical instrument shaped like a pen, known as a DHI implanter, is used to extract hair follicles from the donor area without affecting other hair.
These hair follicles are sent to laboratories for processing into grafts. These processed follicles are then implanted back into the recipient area.
The surgeon takes care to ensure that the hair follicles are implanted in a manner that determines their direction.
What to expect after hair transplantation?
The scalp may feel tender following the surgery, and mild to moderate pain may be experienced, for which the doctor may prescribe medications. Bandages may be required over the surgical site for a few days to prevent inflammation or infection, and antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed.
The transplanted hair typically falls out within 3-4 weeks. New hair growth can be observed after 2-3 months, with more noticeable results typically appearing 6-9 months after the initial transplant, once the transplanted hair has shed